Formulae Handbook for Class 10 Maths and Science
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Geography Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy
Question-1
State any three merits of roadways.
Solution:
The growing importance of road transport is rooted in the following reasons:
- The construction cost of roadways is much lower than that of the railways.
- Its maintenance is also cheap and easy.
- Roads can be built in mountainous areas. The roads can traverse comparatively more dissected and undulating topography.
- Roads can negotiate higher gradients of slopes and as such can traverse mountains such as the Himalayas.
- Road transport is economical in the transportation of a few persons and a relatively smaller amount of goods over short distances.
- It provides door-to-door service, which results in a lower cost of loading and unloading.
- It is used as a feeder to other modes of transport such as they provide a link between railway stations, air, and seaports.
- Road transport connects fields with markets and factories.
- Road transport is useful for the transport of perishable commodities.
Question-2:
Where and why is rail transport the most convenient means of transportation?
Solution:
- Railways can transport larger number of goods and passengers over long distances at an economical cost. Hence, railways are the most convenient means of transport in the vast northern plains of India.
- The flat terrain, dense population, rich agricultural resources and greater industrial activity have favoured the development of railways in this region.
- The northern plains, therefore, have the densest railway network.
- Railways have accelerated the development of industry and agriculture in this region
by providing quick availability of raw materials and distributing the finished products to the markets. - However, in spite of the fact that railways is the most convenient means of transportation in northern plains, a large number of rivers requiring construction of bridges across their wide beds posed some obstacles.
More Resources for CBSE Class 10
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Sanskrit
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Foundation of IT
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions
Question-3
What is the significance of the border roads?
Solution:
The significance of Border Roads is as mentioned below :
- The Border Roads are vital road link along the frontiers of our country.
- These roads are of strategic importance.
- These roads have improved accessibility in areas of difficult terrain mainly in the northern and northeastern border areas.
- They have played a major role in the economic development of these areas.
- These roads are constructed and maintained by the Border Roads Organisation a government of India undertaking which was established in 1960.
Question-4
What is meant by trade? What is the difference between international and local trade?
Solution:
Trade, international and local trade :
(a) The exchange of goods among people, states, and countries is known as trade.
(b) Difference between international and local trade is as given below :
| International Trade | Local trade |
|
(1) The exchange of commodities between two or more countries is termed as international trade. (2) It may take place through sea, air or land routes. (3) Export and import are the components of international trade. (4) Advancement of international trade of a country is an index to its economic prosperity. It is, therefore, considered the economic barometer for a country. (5) The international trade leads to the earning of foreign exchange and benefits for the traders and .exporters in the country. |
(1) Local trade is carried within cities, towns or villages. Exchange of items takes place in local markets where items of local needs are catered to. (2) Local trade mainly takes place through roads, railways, or inland waterways. (3) Sale and purchase are the components of local trade. (4) Advancement of local trade is a sign of economic prosperity of the local people. (5) It does not earn foreign exchange but helps in the fulfillment of the needs of the people. |
Question-5
Why are the means of transportation and communication called the lifelines of a nation and its economy?
Solution:
Today, we are living in the age of communication, using the telephone, television, films, and the Internet. Even books, magazines and newspapers are important means of communication. Various means of transport and communication have reduced distances, bringing the world closer. Modern life is so complex that one has to depend on others. The same is true of the countries as well. No country today can prosper without the co-operation and assistance of others. This requires the movement of goods and materials between countries. Trade provides us with our necessities and also adds to the amenities and comfort of our life. We may also notice that they are rightly called the lifelines of our national economy.
Question-6
Write a note on the changing nature of international trade in the last fifteen years.
Solution:
The nature of international trade in the last fifteen years has changed due to, globalization. Earlier bilateral agreements were made to conduct trade between two countries.
But through globalization, an effort has been made to integrate national economies with the world economy. Now producers from outside countries can sell their goods and services in other countries. Globalisation includes the movement of capital as well as workers from one country to another country. The restrictions on the import of goods have been removed. Under World Trade
The organization, efforts are being made to have multi-lateral agreements for international trade. WTO is regulating the international trade of goods as well as services. Thus international trade has undergone a sea change. The export of agriculture and allied products, ores, minerals, gems, jewellary, chemicals and allied products, engineering goods, and petroleum products have increased. On the other hand import of petroleum and petroleum products, pearls and precious stones, inorganic chemicals, coal, coke have increased too.
The exchange of commodities and goods have been superseded by the exchange of information and knowledge. India has emerged as a software giant at the international level. It is earning large foreign exchange through the export of information technology because of its fast-growing Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) sector.
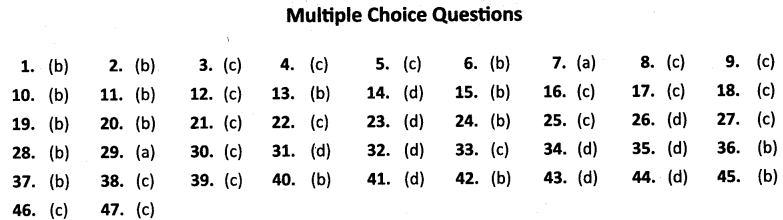
Multiple Choice Questions
NCERT Questions
1. Which one of the following states has the highest road density? [All India 2012]
(a) Goa
(b) Kerala
(c) Karnataka
(d) Gujarat
2. Which one of the following is an inland riverine port? [Delhi 2012]
(a) Kandla
(b) Kolkata
(c) Mumbai
(d) Tuticorin
3. Which one of the following means of transport is used for carrying solids in a slurry form? [Foreign 2012]
(a) Trucks
(b) Railways
(c) Pipelines
(d) Ships
4. Which one of the following groups of cities is connected by National Highway No. 2? [CBSE CCE 2012]
(a) Delhi – Amritsar
(b) Delhi – Mumbai
(c) Delhi – Kolkata
(d) Varanasi – KanniyaKumari
5. Which one of the following National Highways is the longest in India? [CBSE CCE 2012]
(a) NH-1
(b) NH-8
(c) NH-7
(d) NH – 24
6. Which of the following state has the lowest density of roads? [CBSE CCE 2012]
(a) Assam
(b) Jammu and Kashmir
(c) Goa
(d) Rajasthan
7. Which port was develop as a subsidiary port in order to retrieve the growing pressure on the Kolkata port? [CBSE CCE 2012]
(a) Haldia
(b) Paradeep
(c) Kandla
(d) Tuticorin
8. The first class mail includes which one of the following? [Delhi 2011]
(a) Book packets
(b) Registered newspapers
(c) Envelopes and cards
(d) Periodicals and journals
9. By whom are Super Highways being implemented? [Foreign 2011]
(a) CPWD
(b) BRO
(c) NHAI
(d) PWD
10. Which one of the following major ports has been developed to decongest Kolkata port ? [All India 2011]
(a) Kandla
(b) Haldia
(c) Paradip
(d) Marmagao
11. Which two of the following extreme locations are connected by the East-West Corridor ?
(a) Mumbai and Nagpur
(b) Silchar and Porbandar
(c) Mumbai and Kolkata
(d) Nagpur and Siliguri
12. Which mode of transportation reduces trans¬shipment losses and delays ?
(a) Railways
(b) Roadways
(c) Pipeline
(d) Waterways
13. Which one of the following states is not connected with the H.V.J. pipeline?
(a) Madhya Pradesh
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Gujarat
(d) Uttar Pradesh
14. Which one of the following ports is the deepest land-locked and well-protected port along the east coast ?
(a) Chennai
(b) Paradip
(c) Tuticorin
(d) Vishakhapatnam
15. Which one of the following terms is used to describe trade between two or more countries ?
(a) Internal trade
(b) International trade
(c) External trade
(d) Local trade
Additional Questions
16. National Highway-8 connects
(a) Delhi-Bangalore
(b) Chennai-Kolkata
(c) Delhi-Mumbai
(d) Mumbai-Chennai.
17. Indian railways are divided into ………………. zones
(a) 20
(b) 9
(c) 16
(d) 18
18. The longest pipeline connects
(a) Hazira to Kanpur
(b) Saiaya to Jalandhar
(c) Hazira to Jagdishpur
(d) Koyali to Haldia.
19. The total length of Inland navigation waterways of India is
(a) 3,700 km.
(b) 14,500 km.
(c) 7,500 km.
(d) 14,000 km.
20. India’s international trade mainly takes place through
(a) Railways
(b) Seas and oceans
(c) Airways
(d) Roadways
21. The people who make the products come to the consumers by transportation are called ……………
(a) Businessman
(b) Retailers
(c) Traders
(d) Industrialists
22. Which one of the following does not belong to land transport ?
(a) Roads
(b) Railways
(c) Airways
(d) Pipelines
23. Who maintains the District Roads ?
(a) District Magistrate
(b) Municipality
(c) Village Panchayat
(d) Zila Parishad
24. Which one of the following states has the lowest road density ?
(a) Rajasthan
(b) Jammu & Kashmir
(c) Arunachal Pradesh
(d) Kerala
25. The first train was steamed off from
(a) Mumbai to Kalyan
(b) Mumbai to Delhi
(c) Mumbai to Thane
(d) Mumbai to Satara
26. Which one of the following rivers is declared as National Waterway No.1?
(a) Indus
(b) Brahmaputra
(c) Godavari
(d) Ganga
27. Nedimbacherry International Airport is located in which one of the following states ?
(a) Tamil Nadu
(b) Andhra Pradesh
(c) Kerala
(d) Karnataka
28. Raja Sansi International Airport is located in which state?
(a) Jammu & Kashmir
(b) Punjab
(c) Himachal Pradesh
(d) Haryana
29. Which one of the following is not the means of mass communication ?
(a) Cards and envelopes
(b) Radio
(c) Newspaper
(d) Films
30. In which language are maximum number of newspapers published in India?
(a) English
(b) Malayalam
(c) Hindi
(d) Marathi
31. The total network of India’s roadways is about
(a) 2.5 km
(b) 3.5 km
(c) 5.5 million km
(d) 2.3 million km
32. Which one of the following is the longest national highway ?
(a) NH-1
(b) NH-2
(c) NH-5
(d) NH-7
33. The total network of Indian railways is …………..
(a) 60,000 km.
(b) 52,000 km.
(c) 63,221 km.
(d) 65,000 km.
34. Which one of the following ports has a natural harbour and a rich hinterland ?
(a) Chennai
(b) Vishakhapatnam
(c) Paradip
(d) Tuticorin
35. Which one of the following is contributing to large amount of foreign exchange ?
(a) Export of gold Jewellery
(b) Export of petroleum products
(c) Export of engineering goods
(d) Export of information technology
36. The northern terminal city of North-South corridor is
(a) Jammu
(b) Srinagar
(c) Uri
(d) Kanniyakumari
37. Super highways are constructed and maintained by
(a) Central Public Works Department
(b) National Highway Authority of India
(c) Road Transport Corporation of India
(d) State Public Works Department
38. Which one of the following pairs is not correctly matched ?
| Column I | Column II | |
| (a) | First port | (i) Kandla |
| (b) | Biggest port | (ii) Mumbai |
| (c) | A port located at the entrance of a lagoon | (iii) Tuticorin |
| (d) | An inland riverine port | (iv) Kolkata |
| (e) | Oldest artificial port | (v) Chennai |
39. The air transport was nationalised in ……………
(a) 1950
(b) 1975
(c) 1953
(d) 1990
40. Which one of the following is a subsidiary port of Mumbai ?
(a) Tuticorin
(b) Jawaharlal Nehru
(c) Haldia
(d) Vishakhapatnam
41. What is the name given to the International Airport at Kolkata ?
(a) Jawaharlal Nehru
(b) Meenam Bakkam
(c) Rajiv Gandhi
(d) Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose
42. STD refers to
(a) Suburban Telephone dialing
(b) Subscriber Trunk Dialing
(c) Social Telephone Distributor
(d) Speed Telephone Dialing
43. Which one of the following countries has the largest telecom network in Asia ?
(a) China
(b) Japan
(c) Pakistan
(d) India
44. Which one of the following countries is the largest producer of feature films in the world ?
(a) USA
(b) France
(c) Brazil
(d) India
45. Difference between the total value of exports and imports is called …………….
(a) Balance of Payment
(b) Balance of Trade
(c) Surplus Budget
(d) Deficit Balance
46. Which one of the following commodities does not belong to items of export ?
(a) Gems and jewellery
(b) Agriculture and allied products
(c) Fertilizers
(d) Engineering Goods
47. How many people are directly engaged in tourism industry ?
(a) 10 million
(b) 20 million
(c) 15 million
(d) 25 million
ANSWERS